
The Moro reflex is a two-part reflex, initiated when an infant is startled, commonly by a loud sound or a sudden change in position. During the first part of this reflex, the head and neck extend, the arms extend over the head with the palms facing out and the thumbs flexed. During the second part of the reflex, the arms return symmetrically to the body, with hands tightly clenched into fists and the child begins a vigorous cry.
Sucking & Rooting reflex

In this video this child demonstrate the rooting reflex by turning the head in the same direction as the cheek is stroked. The child then "latches on" to the adult's finger and then to her own finger and begins a vigorous sucking action.
Asymmetric tonic neck reflex
(Fencing position)

This sleeping baby is
demonstrating the
asymmetric tonic neck reflex.
Note the head turned to the right with flexion of the left arm and
extension of the right arm.
Palmar grasp

This
baby demonstrates a
palmar grasp by tightly flexing the fingers in response to stimulating
the palm.
Plantar grasp

A plantar grasp is similar to the palmar grasp in that it is the flexion of the toes in response to a stimulus on the sole of the foot.
Babinski reflex
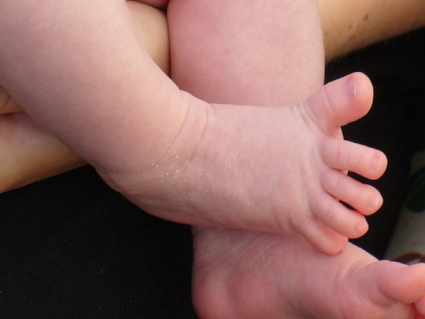
Not to be confused
with the plantar grasp,
the Babinski reflex is a
fanning of the toes along with extension of the great toe in response
to a stimulus along the lateral side of the foot. The finding of
this sign is normal in the first year of life. In contrast, a
"positive" Babinski reflex in an adult is a sign of an upper motor
neuron lesion.
Galant infantile reflex

The Galant infantile reflex is performed when the child is in a prone position. The infant will respond to stroking either side of the back by swinging the hips and legs in the same direction.